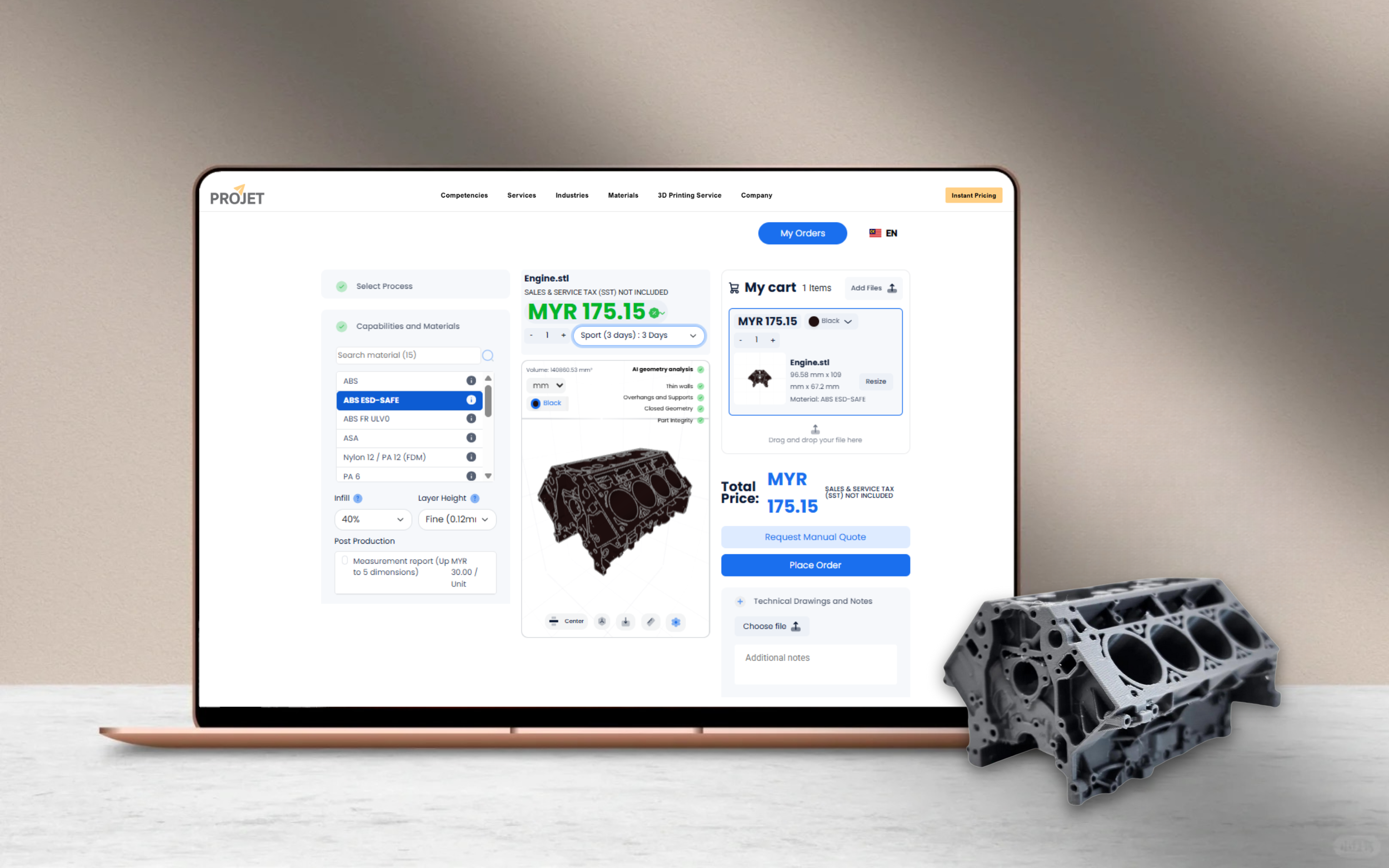
PEEK, PEI, LSR, and Other Material Options for Medical Devices & Equipment
Choosing the Right Plastic for Medical Application
Designing medical components is no small task. Just as there are countless medical procedures, there are also countless types of polymers to choose from — each with different strengths, properties, and certifications. So, which materials are best for your application?
Before we dive in, it’s worth noting that the term “medical grade” can be a bit misleading. It doesn’t refer to a single certification or standard but depends on the intended use and the regulatory requirements your part must meet.

Understanding Medical Material Standards
Medical device manufacturers must comply with numerous standards, but the most relevant for materials is ISO 10993, which covers biocompatibility testing. This standard helps determine whether a material is safe to come into contact with the human body, either externally or internally.
However, there’s no universal list that states which plastics are “approved” or “biocompatible.” Each manufacturer’s resin formulation may vary, and not all sources of the same polymer meet the necessary medical requirements. For instance, one supplier’s ABS might be approved for surgical tools, while another’s is only suitable for toys or power tools.
That’s why it’s crucial to choose your materials — and your manufacturing partner — carefully.
Key Considerations for Medical Thermoplastics
When designing medical parts, look for polymers that are:
- Resistant to heat, chemicals, and corrosion
- Non-absorbent and biologically inert
- Compatible with sterilization methods such as autoclaving
- Safe for skin or body contact, without causing irritation
- Strong, durable, and dimensionally stable
Meeting all of these requirements can be challenging — but several advanced thermoplastics fit the bill.
Top Medical-Grade Thermoplastics
1. Polycarbonate (PC)
When optical clarity is required, polycarbonate is often the top choice. It offers:
Excellent toughness and impact strength
Dimensional stability and chemical resistance
Compatibility with common sterilization methods
You’ll find polycarbonate in transparent components such as housings, fluid reservoirs, and diagnostic devices — anywhere visibility of fluids like blood or medication is needed.
At Projet, medical designers often 3D print prototypes using PC-like materials before moving to machined or injection-molded polycarbonate for full production.

2. Polyetherimide (PEI)
Also known by its trade name Ultem, PEI is a high-performance thermoplastic with excellent strength, heat resistance (up to 180°C), and electrical insulation properties.
PEI is used for:
Handles for surgical instruments
Enclosures for medical devices
Electrical connectors and insulators
It can be sterilized via autoclaving or gamma radiation, making it ideal for reusable medical equipment. Projet offers machining and injection molding of PEI to produce both prototypes and end-use components.

3. Polyetheretherketone (PEEK)
PEEK is one of the most advanced thermoplastics available today. Lightweight, strong, and biocompatible, it’s frequently used in medical and dental implants such as:
Spinal cages and joint replacements
Bone screws and fixation devices
Dental crowns and bridges
PEEK maintains its mechanical properties even under extreme temperatures and sterilization cycles. It’s also radiolucent, meaning it doesn’t interfere with X-rays or imaging.
Projet routinely 3D Printing PEEK parts for demanding medical applications, from functional prototypes to production components.
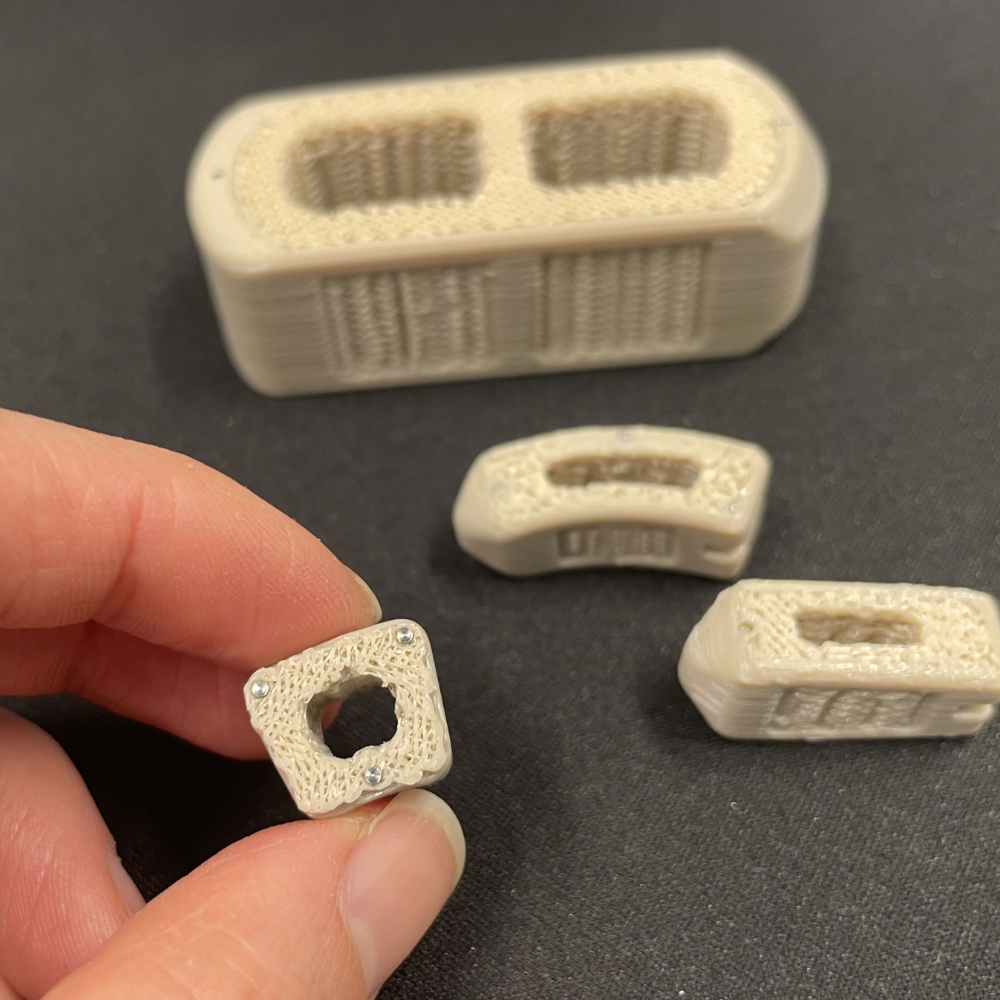
4. Silicone and Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR)
Silicone isn’t just for cooking utensils or sealants — it’s a powerhouse material for medical devices. Available in various hardness levels, it can be soft and flexible or firm and durable, depending on the application.
Key advantages include:
Temperature tolerance from –55°C to 210°C
Resistance to water, solvents, and acids
Excellent biocompatibility and comfort against skin
Suitability for prosthetics, seals, gaskets, and surgical models
At Projet, we offer both 3D printing and Vacuum Casting in liquid silicone rubber (LSR). This allows for rapid prototyping of complex geometries and smooth transition to production-scale manufacturing. For optical applications, Optical LSR (OSLR) provides superior clarity and light transmission — perfect for medical lenses, lighting components, and transparent enclosures.
Partnering with Projet
The medical industry demands materials that balance safety, strength, and sterility. At Projet, we understand these challenges. Our expertise in 3D printing, CNC machining, and injection molding allows us to deliver components that meet the highest standards for biocompatibility and performance.
Partner with Projet to bring your next medical innovation to life with materials you can trust.
3D Printing Services
Instant Price